How to choose electrical fittings and cable glands: quality and certifications
14 Apr , 2023
Choosing fittings and cable glands to protect electrical cables is critical in creating efficient and safe installations. This article explores the various aspects to consider when buying cable glands and fittings. Also, we will include a few examples that we hope you will find helpful.
How to choose a conduit fitting
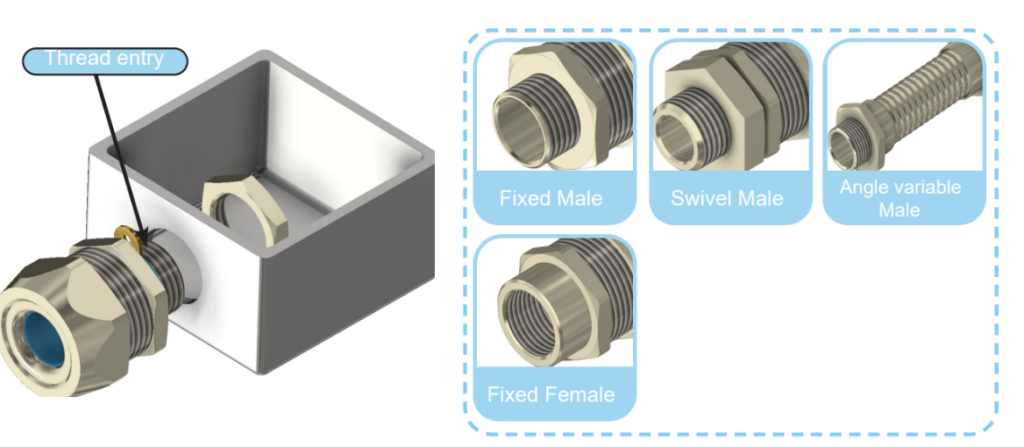
A conduit fitting connects junction boxes or the thread entry in the wall to external elements (such as flexible conduits, corrugated plastic conduits, or rigid conduits).
A few examples of Euro2000 fittings are flexible conduit fittings and quick-coupling fittings for rigid conduits etc.
Choosing safe and high-quality fittings requires checking if the products are certified and according to which standards. Our metal fittings and flexible conduits are certified according to “EN IEC 61386-1 Conduit systems for cable management – Part 1: General requirements” and “Mechanical Protection Tubing (MPT) and Fittings – UL 1696.” The rigid (metallic) conduit system and related fittings are certified according to IEC 61386-1:2008/AMD1:2017, IEC 61386-21:2002, EN 61386-21:2004 + A11:2010, EN 61386- 1:2008 + A1:2019. Nylon fittings, connectors, and corrugated flexible conduits are certified according to “Mechanical Protection Tubing (MPT) and Fittings – UL 1696.”
Another aspect to consider is the ease of use. Our innovative system allows conduits and fittings to be assembled and disassembled conveniently and quickly.
How to choose cable glands
A cable gland helps to hold the cable from external disturbances (such as external forces, vibrations, etc.), ensures IP sealing (e.g., water, dust) as well as provides cable grounding, connection, insulation, and protection allowing the cable to be mounted in a junction box via the threaded entry.
When choosing cable glands, it is also essential to consider the various certifications and handiness. Our quality control has tested our metal cable glands according to “Cable Glands for Electrical Installations CEI EN 62444, IEC 62444.” The special EMW cable glands (designed for electromagnetic protection) feature a sealed land hermetic locking for armored cables, protecting the cable from electromagnetic interference originating from other devices in the system.
Nylon cable glands are used in a wide range of applications and can withstand the highest levels of strain and vibration. We offer a special nylon spiral cable gland for use where it is possible to bend cables. It allows cables to be bent within a maximum radius to avoid damage. Browse all Euro 2000 cable glands available in the catalog.
Keep in mind the option of the cable gland fitting
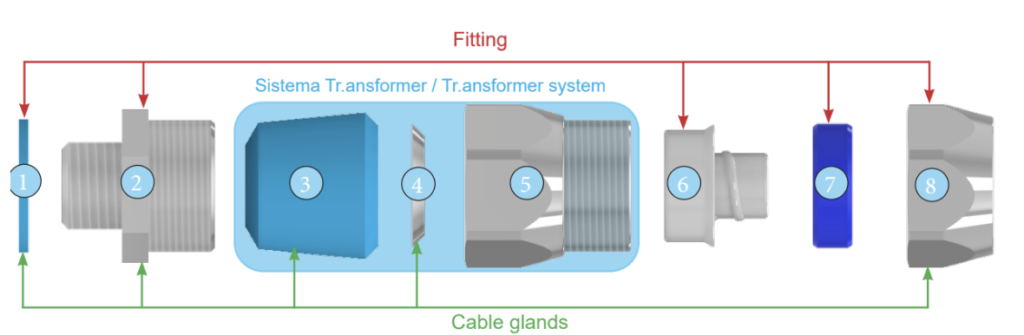
A cable gland fitting acts as both a fitting and a cable gland. Euro2000 cable glands meet both the fitting and the cable gland’s requirements. One of the main features of protection systems is that the fittings must hold the conduit from external pulls and vibrations, just as the cable gland must hold the flexible cable. When choosing fitting cable glands,, we recommend adopting the same precautions listed above that is paying attention to certifications, quality, and innovation in the manufacturing of each component. Our cable gland fittings have been designed as modular systems. Our standard fittings can be converted into cable gland fittings with the help of our patented Tr.ansformer System kit shown in Figure 1.
Types of threads and threaded entries
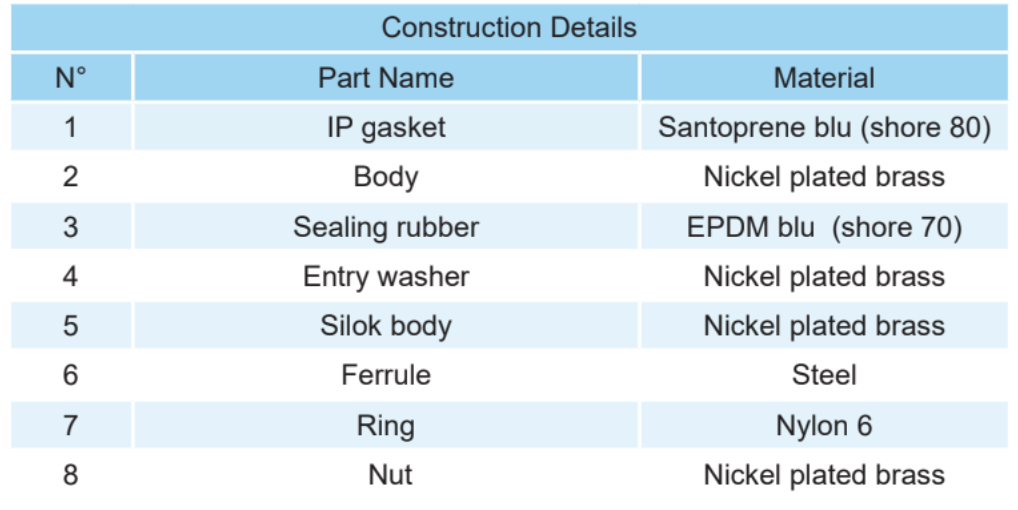
In those applications where the protection system needs to connect to another system, the cable glands and fittings connect through a junction box via a male thread that goes through a hole and is tightened using a locknut (see Fig. 2). There are two types of entry threads: male and female (see fig. 3). Euro2000 has available various male threads: fixed male threads, swivel male threads, and variable angle male threads (see Fig. 3).
The parallel or cylindrical threads available with IP gasket are the following: metric ISO (ISO 965-1), GAS thread (ISO 228-1), Pg thread (DIN 40430), and UN and UNEF threads (ANSI/ASME B1.1). The tapered threads with IP protection without an IP gasketc capable of ensuring pressure sealing on the threads are the NPT threads (ANSI/ASME B1.20.1), and ISO tapered gas threads (ISO 7-1).